NanoAndMore Europe proudly sponsors the XIII Workshop on Applications of Scanning Probe Microscopy – STM/AFM 2025, which will be held in Zakopane from 26 - 30 November 2025 https://nanosam.pl/stmafm2025/
The Workshop is organized by the Centre for Nanometer-scale Science and Advanced Materials (NANOSAM) https://nanosam.pl/ of the Faculty of Physics, Astronomy, and Applied Computer Sciences, Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland.
Unfortunately, we are unable to attend in person this year, but we encourage all participants to look at our #AFMprobes flyer in the conference bag for the latest updates and offers from NanoAndMore.
If you have any questions on the #AFMtips by BudgetSensors, MikroMasch, OPUS, NanoWorld, NANOSENSORS, nanotools, sQube Colloidal AFM Probes and original Olympus #microcantilvers we offer, please free to contact us.
The NanoAndMore team wishes the organizers and all attendees a successful workshop filled with inspiring scientific exchange. A quick look at the webcam on Krupowki Street shows that there is plenty of snow in Zakopane this year, making the non-scientific activities especially appealing!
#nanoandmore #scanningprobemicroscopy #atomicforcemicroscopy #nanoscience #AFM #SPM #nanoscale #nanoscience #appliedphysics #materialsscience #materialsreserach #AFMtips #SPMtips #NANOSAM



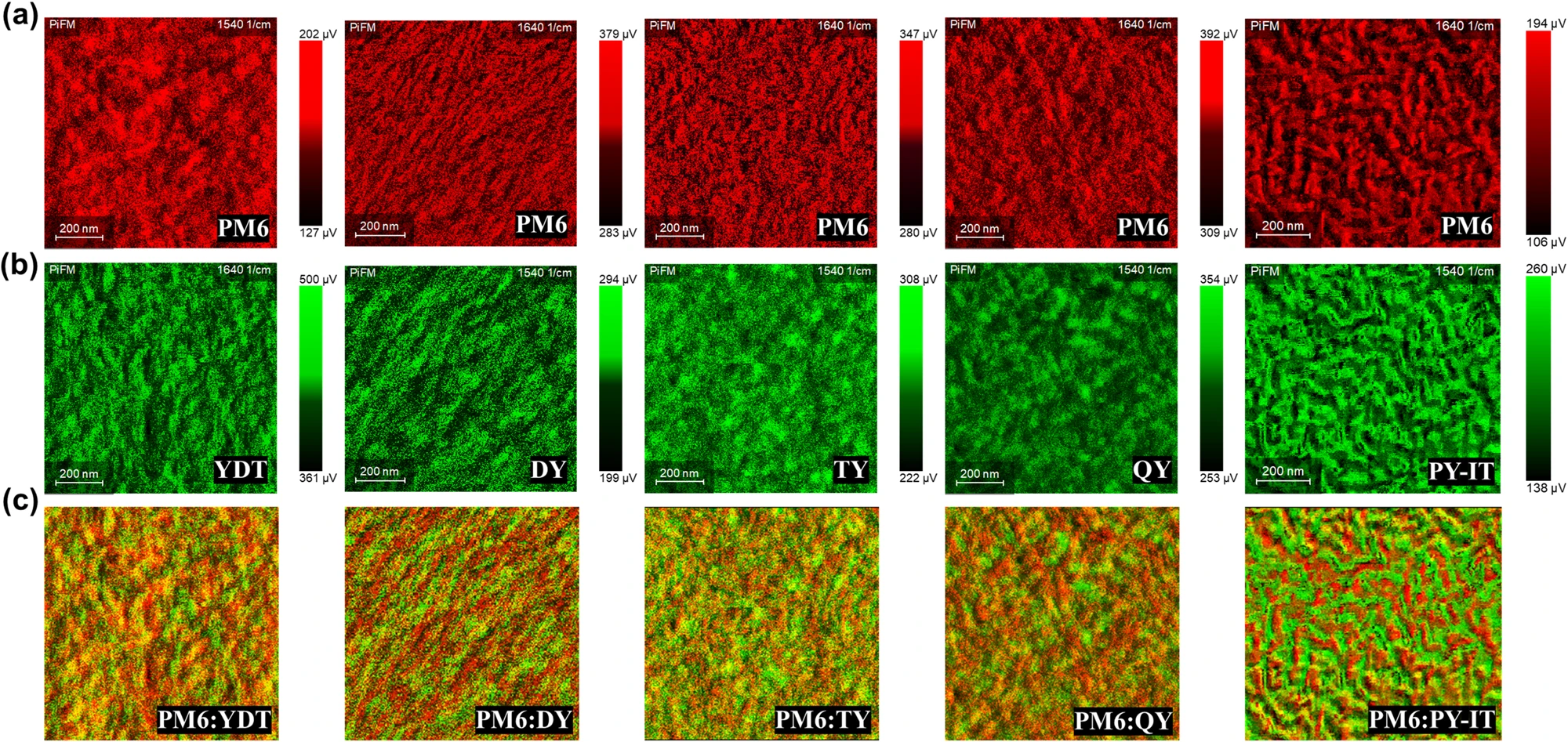
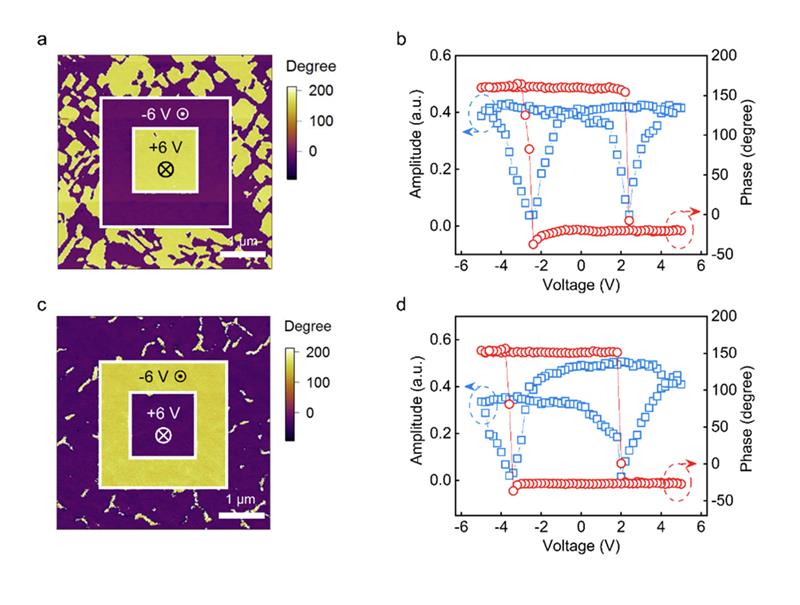
In their 2023 Nature Communications article, “Precise synthesis and photovoltaic properties of giant molecule acceptors,”Hongmei Zhuo, Xiaojun Li, Jinyuan Zhang, Can Zhu, Haozhe He, Kan Ding, Jing Li, Lei Meng, Harald Ade, and Yongfang Li report a transformative advance in organic solar cell design. By precisely linking multiple small-molecule acceptors into “giant molecule acceptors” (GMAs), the researchers enhanced exciton diffusion and charge transport. Their three-unit GMA reached an impressive power conversion efficiency of 16.32%, highlighting how molecular architecture directly influences photovoltaic performance.
Read the full article here: https://www.nanosensors.com/blog/nanosensors-afm-probes-enable-nanoscale-insights-into-organic-photovoltaics/


Celebrating science at the scale of 10⁻⁹ meters — where the smallest innovations create the biggest impact.
There’s hardly a better day in the year to capture some beautiful #AFM images and celebrate the tools that make nanoscience possible. At NanoAndMore USA, we’re proud to support researchers worldwide with the industry’s widest selection of #AFMprobes — trusted by leading labs, universities, and manufacturers across the globe!
#1 AFM Tips Shop Worldwide - https://www.nanoandmore.com/
#AFM #AFMProbes #Nanotechnology #NationalNanotechDay #10Eminus9 #Nano #AtomicForceMicroscopy


MikroMasch® HQ: CSC37/No Al probes were recently used in a study by Lee, Shrotriya and Espinosa-Marzal titled “Responsiveness of Charged Double Network Hydrogels to Ionic Environment”, published in Advanced Functional Materials. In their work, interactions between the hydrogel and the ionic environment are shown to induce structural changes – those in turn impact surface properties, which are characterized using in-liquid AFM and chemically functionalized tips.
Illustration of the AgPAAc hydrogel microstructure and its intermolecular forces in response to added ions. The microstructure comprises an agarose scaffold (black) with interconnecting polyacrylic acid (orange/yellow). The dark blue block represents the AFM tip (unmodified (-) or functionalized (+)). The double network strengthens hydrogels, with distinct contributions of the two polymers and their concentrations. Hydrogel charging is regulated by the limited swelling of the double network, the weak polyelectrolyte effect, and charge screening. A tunable behavior in response to salt concentration is enabled and depends on composition. A) 2Ag and 2Ag5.6PAAc hydrogels: High swelling and charge density; Competition between electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding. B) 3Ag5.6PAAc hydrogels: Intermediate swelling and charge density. Greater tunability of adhesion and surface stiffness by adding salt compared to 2Ag5.6PAAc DN hydrogels. Electrostatic forces outweigh hydrogen bonding. C) 3Ag9PAAc hydrogels: High toughness, low swelling, and low charge density. Increasing the polyacrylic concentration in the double network reverses the change of surface stiffness and adhesion upon the addition of salt due to charge regulation.
Shop here: https://www.spmtips.com/afm-tip-hq-csc37-no-al
#MikroMasch #HighResolutionAFMProbes


NanoWorld® at the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society of Japan (Nara, Sept 24–26, 2025)
Hello from Nara! NanoWorld® is exhibiting with our partner NanoAndMore Japan at the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society of Japan. If you’re working at the frontiers of biophysics—membranes, proteins, cell mechanics, or high-resolution imaging in liquid—come by booth #36 to discuss the best AFM probe for your experiment.
We’ll be showcasing the Pointprobe® and Arrow™ series—trusted worldwide for consistency, tip sharpness, and batch-to-batch reproducibility—plus short-cantilever options for fast dynamics. Our team can help you choose geometries and parameters that improve stability, SNR, and throughput on your instrument.
Let’s connect in Nara and move your research forward—one high-quality probe at a time.
Where: NanoAndMore Japan, Booth #36 When: Sept 24–26, 2025 • Nara Prefectural Convention Center


NanoWorld® AG CEO Manfred Detterbeck will be at the NanoAndMore Japan booth at the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society of Japan held from September 24– 26, 2025 at Nara Prefectural Convention Center.
Will we meet you there too?

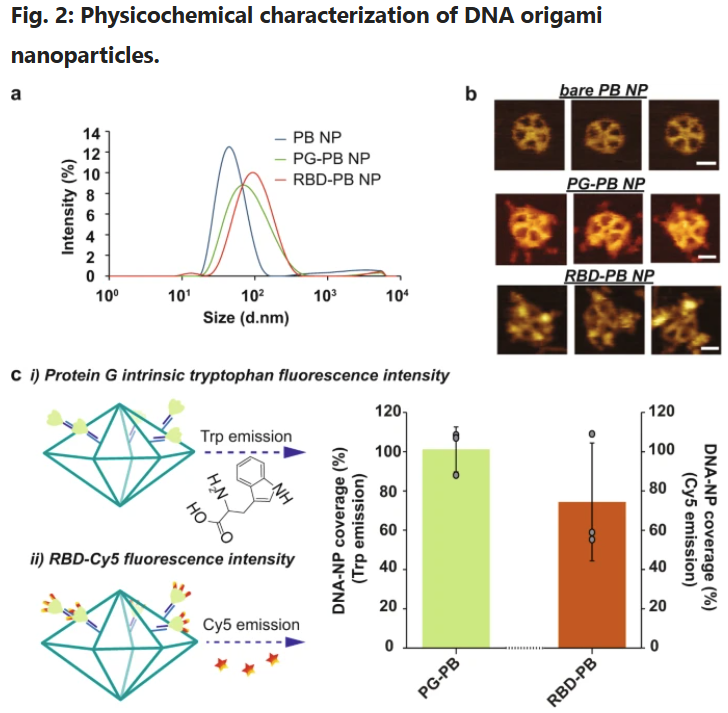
A study recently published in Communications Biology (Nature Portfolio) by Esra Oktay, Farhang Alem, Keziah Hernandez, Michael Girgis, Christopher Green, Divita Mathur, Igor L. Medintz, Aarthi Narayanan, and Rémí Veneziano introduces an innovative DNA origami–based nanovaccine platform targeting the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2.
Their findings highlight the potential of rationally engineered DNA nanoparticles to elicit strong and durable immune protection.



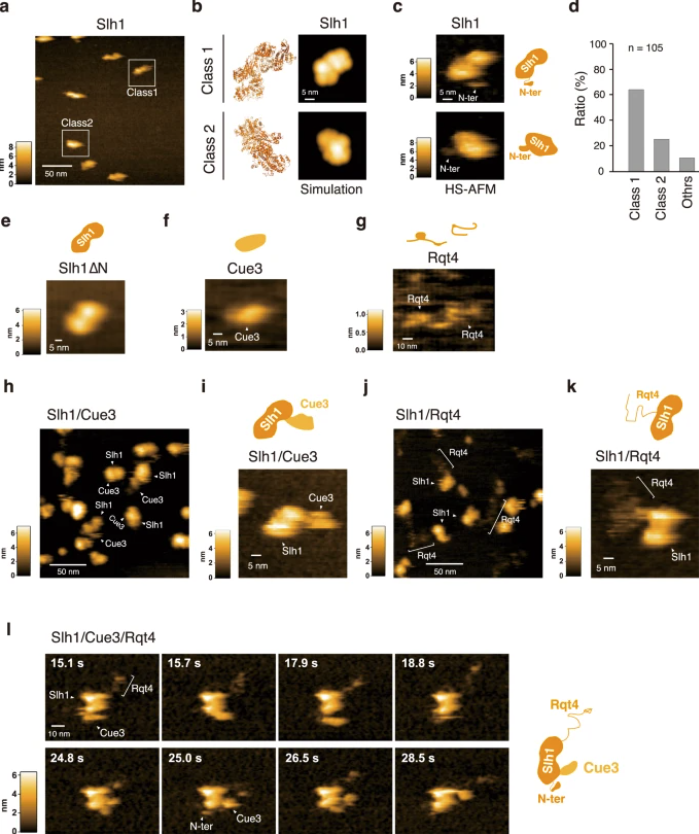
Matsuo et al., recently published a landmark study in Nature Communications (vol. 14, article 79, Jan 10 2023). , looking at how cells recognize and resolve ribosome collisions—a critical event in obeying translational fidelity and avoiding protein quality control failure.
The researchers employed a combination of molecular genetics, biochemical assays, ubiquitin-binding studies, and advanced imaging. Key steps included mutational deletion of ubiquitin‐binding domains in RQT subunits, affinity assays for K63-linked ubiquitin chains, and highspeed atomic force microscopy (HSAFM) to visualize complex behavior at the molecular level. Notably, they used intrinsically disordered regions of Rqt4 mapped by realtime HSAFM.

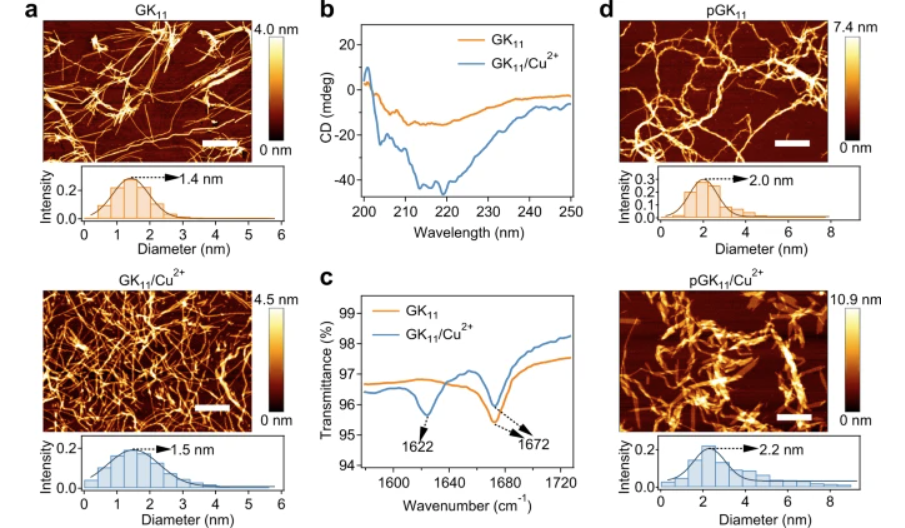
Bin Xue et al. have presented a novel class of biomimetic hydrogels that simultaneously exhibit high stiffness, toughness, fatigue resistance, and ultrafast mechanical recovery—properties that are notoriously difficult to combine in conventional polymeric systems. Their design is inspired by the architecture of mussel foot proteins and is centered around self-assembling peptide fibres termed “picot fibres”, which act as hierarchical load-bearing domains.
Read more...







One of the co-inventors of AFM! Born on July 20th 1947, in Frankfurt, West Germany, Prof. Binnig has made extensive contributions to scanning probe microscopy techniques, including AFM and STM. For his work on STM, he was distinguished with the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics, shared with Heinrich Rohrer.


On July 9th 2008 this calibration image was acquired by NASA’s Phoenix Mars Lander, making it the first AFM image acquired on another planet! The inclusion of an AFM, as part of Phoenix’s Microscopy, Electrochemistry and Conductivity Analyzer, allowed for imaging at an unprecedented resolution, offering a 20-fold increase compared to the on-board optical microscope.
Photo credit: ASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/University of Neuchatel
#AFMprobes #AFM #AtomicForceMicroscopy #Mars